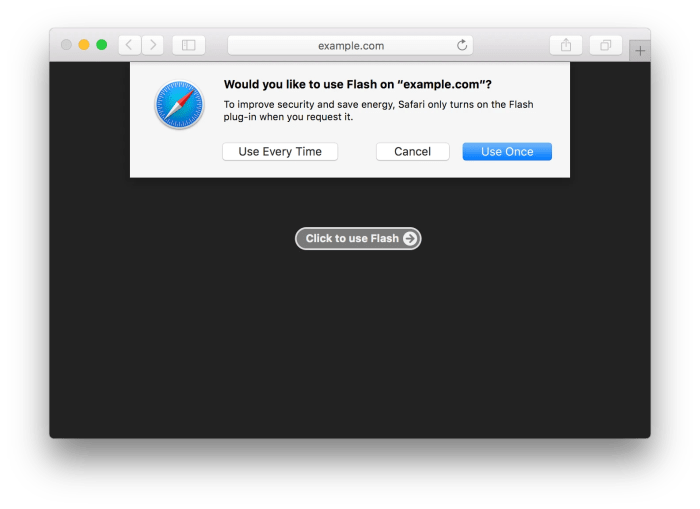
Flash deactivated in Safari 10 by default marked a significant shift in web browsing, signaling a move away from a technology riddled with security vulnerabilities and performance issues. This decision, driven by Apple’s commitment to a safer and smoother online experience, had a profound impact on users and developers alike.
The prevalence of Flash content in the early days of the internet was undeniable. Websites relied on it for interactive elements, animations, and multimedia playback. However, as technology evolved, Flash’s limitations became increasingly apparent. Security breaches and slow loading times became commonplace, prompting a search for alternative solutions.
Case Studies and Examples
The shift away from Flash has impacted user experience on various websites. Examining specific cases provides insights into the challenges and benefits of this transition.
User Experience Comparison
This table compares the user experience before and after Flash deactivation on popular websites.
| Website | User Experience Before Flash Deactivation | User Experience After Flash Deactivation |
|---|---|---|
| YouTube | High-quality video playback, interactive features like full-screen mode and annotations, but sometimes slow loading and potential security vulnerabilities. | Improved performance, smoother playback, and enhanced security, but some features like interactive elements might be missing or require updates. |
| Interactive games and animations, but could lead to slow loading times and compatibility issues on certain devices. | Streamlined user interface, faster loading times, and improved compatibility across various devices, but some interactive elements might be missing. | |
| Adobe Flash Player Website | Flash-based content, including interactive demos and tutorials, but could face compatibility issues and security risks. | Content migrated to HTML5, ensuring compatibility and security, but some older features might be unavailable. |
Successful Migrations from Flash to HTML5
Websites that successfully migrated from Flash to HTML5 have generally experienced improved performance, enhanced security, and wider compatibility.
- YouTube: YouTube transitioned from Flash to HTML5 for video playback, resulting in faster loading times, smoother playback, and enhanced security. They also introduced features like offline playback and adaptive streaming, further improving user experience.
- Facebook: Facebook transitioned from Flash to HTML5 for its games and animations, leading to improved performance, reduced loading times, and enhanced compatibility across different devices. This transition also eliminated security vulnerabilities associated with Flash.
- Adobe: Adobe migrated its Flash Player website to HTML5, ensuring compatibility and security. The transition also allowed them to introduce new features like interactive tutorials and demos, improving the overall user experience.
Websites Still Relying on Flash, Flash deactivated in safari 10 by default
Some websites still rely on Flash, facing challenges related to compatibility, security, and performance.
- Older Games: Some older games, particularly those developed before the widespread adoption of HTML5, still rely on Flash. This can lead to compatibility issues on modern browsers and devices, limiting their accessibility to a wider audience.
- Specialized Applications: Certain specialized applications, like some medical imaging software or industrial control systems, might still require Flash due to its specific capabilities. However, this reliance poses security risks and compatibility challenges.
- Legacy Websites: Websites that have not been updated to use HTML5 might still rely on Flash, leading to performance issues, security vulnerabilities, and compatibility problems on modern browsers and devices.
Future Trends and Considerations: Flash Deactivated In Safari 10 By Default
The sunsetting of Flash has ushered in a new era for web technologies, driven by advancements in browser capabilities, user expectations, and the rise of open web standards. This section explores the ongoing evolution of web technologies and how they have replaced Flash, along with emerging trends that will shape the future of web development.
Impact of Web Technologies on Flash
The development of web technologies has significantly impacted the use of Flash. HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScript have become powerful alternatives to Flash, providing a more versatile and secure platform for web development. HTML5 offers rich multimedia capabilities, including video and audio playback, while CSS3 provides advanced styling options, and JavaScript enables interactive and dynamic web experiences.
Emerging Trends in Web Design and Development
The web design and development landscape is constantly evolving, with new trends emerging to enhance user experience and web performance. These trends have largely replaced Flash as the preferred technology for creating interactive and engaging web content.
- Responsive Web Design: Websites designed to adapt to different screen sizes and devices are now the norm. This trend has made Flash obsolete, as its static nature was not compatible with responsive design principles.
- Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): PWAs are web applications that offer a native app-like experience, blurring the lines between web and mobile apps. This trend has further reduced the need for Flash, as PWAs leverage web technologies to deliver a seamless user experience across platforms.
- Single-Page Applications (SPAs): SPAs are websites that load a single HTML page and dynamically update content using JavaScript. This approach offers a faster and more interactive user experience, making Flash less relevant.
Advancements in Browser Technology
Modern browsers are constantly being updated with new features and security enhancements, further diminishing the need for Flash. These advancements have significantly improved web performance, security, and user experience.
- WebGL: WebGL enables web developers to create high-performance 3D graphics and animations directly in the browser, eliminating the need for Flash-based solutions. This has opened up new possibilities for interactive web experiences.
- WebAssembly: WebAssembly is a low-level bytecode format that enables web developers to run high-performance applications in the browser. It is a powerful alternative to Flash, allowing for faster execution and improved performance.
- Web Workers: Web Workers allow web developers to run JavaScript code in the background, improving the responsiveness of web applications. This feature has significantly reduced the reliance on Flash for complex tasks that could potentially slow down the browser.
Final Conclusion
The deactivation of Flash in Safari 10 was a watershed moment, accelerating the transition to HTML5 and ushering in a new era of web development focused on security, performance, and cross-platform compatibility. While the initial adjustment period posed challenges for some users and developers, the long-term benefits of this shift are undeniable. The web has become a safer, faster, and more accessible space, paving the way for innovative web experiences that are both engaging and reliable.
While Safari 10 users are adjusting to the default deactivation of Flash, gamers are getting excited about the halo wars 2 release date confirmed beta launches today. This means that even with Flash deactivated, you can still enjoy the latest gaming news and get your hands on the beta.
However, if you need to access a Flash-based website for other purposes, remember to enable it in Safari’s settings.
 Securesion Berita Informatif Terbaru
Securesion Berita Informatif Terbaru