Chrome freeze non important flash files – a frustrating experience for many web users. Imagine clicking a link, eagerly awaiting a page to load, only to be met with a frozen screen, a spinning cursor, and the dreaded “Chrome is not responding” message. This can happen due to various factors, including resource-intensive web pages, outdated browser extensions, or even those pesky Flash files that linger on the web, remnants of a bygone era.
While Flash has largely been phased out, it still exists in some corners of the internet. These files can cause performance issues, especially when they are outdated or corrupted. This article delves into the complex relationship between Chrome freezes and Flash files, exploring how these seemingly innocuous files can wreak havoc on your browsing experience. We’ll also provide troubleshooting tips, alternative browser options, and insights into the evolving landscape of web development, all with the aim of helping you reclaim a smooth and efficient browsing experience.
Understanding Chrome Freeze: Chrome Freeze Non Important Flash Files
Chrome freeze refers to a state where the browser becomes unresponsive, and all actions, including page loading, scrolling, and clicking, are halted. It is different from slow performance, where the browser operates sluggishly but still responds to user input.
Chrome freezes can be triggered by various factors, including:
Common Scenarios That Trigger Chrome Freezes
Chrome freezes can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- High CPU usage: When Chrome consumes a large amount of CPU resources, it can lead to freezes, especially if other programs are also demanding CPU power.
- Memory overload: If Chrome uses too much RAM, it can slow down or freeze, particularly on systems with limited memory.
- Outdated browser version: Using an outdated version of Chrome can introduce bugs and vulnerabilities that might cause freezes.
- Corrupted browser data: Damaged or corrupted browser files, such as user profiles or extensions, can contribute to freezes.
- Overloaded tabs: Opening numerous tabs, especially those with heavy content like videos or animations, can put a strain on Chrome’s resources and cause freezes.
- Resource-intensive extensions: Extensions that consume significant resources can lead to freezes, especially if multiple extensions are running simultaneously.
- Hardware issues: Problems with the computer’s hardware, such as a failing hard drive or insufficient RAM, can contribute to Chrome freezes.
- Malware or viruses: Malicious software can infect the system and interfere with Chrome’s functionality, causing freezes.
- System instability: Issues with the operating system, such as a corrupted system file or insufficient disk space, can also cause Chrome freezes.
User Experience During a Chrome Freeze, Chrome freeze non important flash files
When Chrome freezes, the user will experience a complete lack of responsiveness. The browser window will appear frozen, and all actions, including scrolling, clicking, and typing, will be halted. The user will not be able to interact with the browser in any way, and the only option might be to force quit the browser or restart the computer.
Flash Files and Chrome Freeze
Flash files, a technology once widely used for interactive content and animations, have been known to contribute to Chrome freezes. While Adobe Flash Player has been officially discontinued and is no longer supported, its legacy continues to impact browser performance.
Flash Files and Chrome Freeze
Outdated or corrupted Flash files can significantly impact Chrome’s performance, leading to freezes and slowdowns. This is because Flash content often requires significant processing power and resources. When Flash files are outdated or corrupted, they may not function properly, causing the browser to struggle and potentially freeze.
- Outdated Flash Player: When using an outdated version of Flash Player, the browser may encounter compatibility issues with newer websites and applications. This can lead to slow loading times, crashes, and freezes.
- Corrupted Flash Files: Corrupted Flash files can cause various problems, including freezes, crashes, and unexpected behavior. This is because the browser may struggle to interpret and execute the corrupted code, leading to performance issues.
- Resource-Intensive Flash Content: Some Flash files are designed to be highly interactive and visually appealing, requiring significant processing power and resources. This can strain the browser’s resources, particularly on older or less powerful computers, leading to freezes and slowdowns.
Troubleshooting Techniques
Chrome freezes can be frustrating, especially when they’re related to Flash files. Fortunately, there are several troubleshooting techniques you can use to identify and resolve these issues.
Identifying and Disabling Flash Files
Flash files can be a common source of Chrome freezes. Identifying and disabling these files can often resolve the issue.
Here’s how to identify and disable Flash files within Chrome settings:
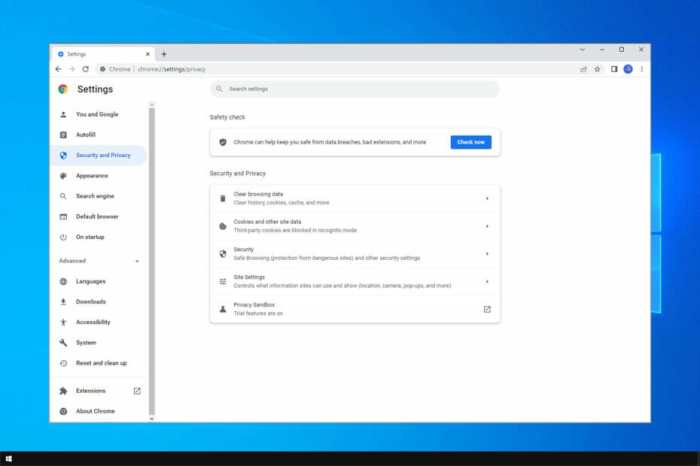
* Open Chrome Settings: Click the three dots in the top-right corner of your browser window, and select “Settings”.
* Navigate to Privacy and Security: Scroll down to the “Privacy and security” section and click on “Site settings”.
* Select Flash: Click on “Flash” to view the settings for Flash content.
* Manage Flash Settings: You’ll see a list of websites that have requested to use Flash. You can choose to “Block” or “Allow” Flash for specific websites.
* Disable Flash Globally: If you’re experiencing frequent freezes related to Flash, you can disable Flash globally by clicking the “Block sites from running Flash” toggle switch.
Alternative Methods for Handling Flash Content
If disabling Flash is not an option, you can try these alternative methods for handling Flash content:
* Use a Flash Player Plugin: You can use a Flash Player plugin to handle Flash content. However, this can also be a source of freezes if the plugin is outdated or corrupted.
* Find Alternative Content: If possible, find alternative content that does not require Flash. Many websites now offer HTML5 versions of their content that do not require Flash.
* Contact the Website Owner: If you’re encountering a problem with a specific website, contact the website owner and report the issue. They may be able to provide a solution or update their website to remove the need for Flash.
Chrome Updates and Flash Compatibility
Chrome updates play a crucial role in addressing Flash-related issues, enhancing security, and improving overall browser performance. As Chrome evolves, its compatibility with Flash has been dynamically adapting, reflecting the changing landscape of web technologies.
Chrome’s Development and Flash Compatibility
The development of Chrome has significantly impacted Flash compatibility over time. Initially, Chrome embraced Flash as a vital web technology. However, as HTML5 gained traction, Chrome gradually reduced its reliance on Flash, prioritizing HTML5 for richer multimedia experiences. This shift was driven by several factors:
- Security Concerns: Flash has been known for its security vulnerabilities, making it a target for attackers. Chrome’s focus on security led to a reduced reliance on Flash, mitigating potential risks.
- Performance Improvements: HTML5 offered performance advantages over Flash, particularly in terms of loading times and resource consumption. This shift towards HTML5 resulted in a smoother browsing experience for users.
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: HTML5 provided greater cross-platform compatibility, ensuring a consistent experience across various devices and operating systems. This factor further solidified the move away from Flash.
Ensuring Compatibility with Latest Flash Updates
To ensure your Chrome version is compatible with the latest Flash updates, consider the following:
- Automatic Updates: Chrome automatically updates itself in the background, ensuring you have the latest security patches and compatibility improvements. Keep your Chrome browser up-to-date to benefit from these updates.
- Manual Updates: If automatic updates are disabled, you can manually check for updates by going to “Settings” -> “About Chrome.” Chrome will automatically download and install any available updates.
- Flash Plugin Management: Chrome allows you to manage Flash plugins, enabling or disabling them based on your preferences. You can access this setting by going to “Settings” -> “Privacy and security” -> “Site settings” -> “Flash.”
Alternative Browser Options
If you’re experiencing frequent Chrome freezes due to Flash, switching to a browser with minimized or eliminated Flash support might be a good solution. Here’s a look at some popular alternatives and their features.
Browser Alternatives and Features
Switching to a different browser can provide a smoother browsing experience, especially if you’re encountering frequent freezes due to Flash. Here are some popular alternatives and their features:
- Firefox: Firefox, developed by the Mozilla Foundation, is known for its strong privacy features and extensive customization options. It has a built-in Flash player, but it’s often updated to address security vulnerabilities. You can disable Flash in Firefox’s settings, which can improve performance.
- Safari: Apple’s Safari browser is designed for macOS and iOS devices and is known for its speed and integration with Apple’s ecosystem. It doesn’t have built-in Flash support and relies on Apple’s own WebKit rendering engine.
- Microsoft Edge: Microsoft Edge is the default browser for Windows 10 and is designed to be fast and secure. It doesn’t have built-in Flash support and uses its own rendering engine.
- Opera: Opera is a fast and feature-rich browser known for its built-in VPN and ad blocker. It has a built-in Flash player, but you can disable it in the settings.
- Brave: Brave is a privacy-focused browser that blocks ads and trackers by default. It uses Chromium, the same engine as Chrome, but with additional privacy features. Brave doesn’t have built-in Flash support.
Comparing Features and Performance
These alternative browsers offer a range of features and performance levels that can be compared to Chrome:
- Performance: Browsers like Safari and Edge are known for their speed and efficiency, while Firefox and Opera offer a balance of features and performance.
- Security: All of these browsers prioritize security, with features like built-in ad blockers, anti-tracking measures, and regular security updates.
- Customization: Firefox offers extensive customization options, while Chrome and Opera have a wide range of extensions and add-ons.
- Privacy: Brave and Firefox are known for their privacy-focused features, while other browsers like Safari and Edge also offer privacy controls.
Benefits of Switching
Switching to a different browser can provide several benefits:
- Improved Performance: By eliminating or minimizing Flash support, you can potentially experience faster browsing speeds and fewer freezes.
- Enhanced Security: Some browsers have built-in security features like ad blockers and anti-tracking measures, which can help protect your privacy and security.
- Greater Customization: Some browsers offer more customization options, allowing you to tailor the browsing experience to your preferences.
- Improved Privacy: Certain browsers prioritize privacy by default, offering features like built-in VPNs and ad blockers.
System Resources and Chrome Performance
Chrome’s performance is directly influenced by the resources available on your computer. These resources include the computer’s processing power, memory (RAM), and storage space. When Chrome is running, it utilizes these resources to load web pages, run extensions, and handle other tasks.
Resource-Intensive Flash Files and Chrome Performance
Flash files, especially complex animations and interactive content, can be highly resource-intensive. When Chrome encounters such files, it needs to allocate more processing power and memory to handle them. This can lead to a significant strain on the system, resulting in slow performance and even browser freezes.
Managing System Resources for Improved Chrome Performance
- Close Unused Tabs and Extensions: Regularly close tabs you’re not actively using and disable extensions you don’t need. This frees up resources for Chrome to operate more efficiently.
- Limit Background Processes: Background processes can consume significant resources, impacting Chrome’s performance. Minimize the number of programs running in the background.
- Upgrade Hardware: If your computer is struggling to handle Chrome’s demands, consider upgrading your RAM or processor. This can provide a significant performance boost.
- Use Chrome’s Task Manager: Chrome’s built-in task manager allows you to identify resource-intensive tabs and extensions. You can then choose to close or disable them.
Security Considerations
Flash files, while once ubiquitous, have become a significant security concern due to their inherent vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to your system, steal your data, or even take control of your computer. Understanding the security implications of Flash and how Chrome safeguards your browsing experience is crucial for maintaining a secure online environment.
Chrome’s Security Features
Chrome incorporates various security features designed to mitigate the risks associated with Flash. These features include:
- Sandboxing: Chrome isolates Flash content within a secure sandbox environment, preventing it from accessing sensitive system resources or interacting with other applications. This isolation limits the damage a compromised Flash file can inflict.
- Automatic Updates: Chrome automatically updates Flash to the latest version, patching security vulnerabilities as they are discovered. This helps ensure that your Flash player is protected against the most recent threats.
- Flash Blocker: Chrome’s built-in Flash blocker prevents Flash content from running unless you explicitly allow it. This reduces the risk of encountering malicious Flash files by limiting their exposure.
- Site Isolation: Chrome isolates websites from each other, preventing one site from accessing data or resources belonging to another. This helps to contain the impact of a security breach on a single website, preventing attackers from spreading their malicious activity across your browsing session.
Best Practices for Secure Browsing
While Chrome’s security features provide a strong defense against Flash-related threats, it’s essential to adopt best practices to further enhance your online security:
- Keep Your Software Updated: Regularly update your operating system, browser, and other software to patch vulnerabilities and receive the latest security enhancements.
- Be Cautious of Suspicious Websites: Avoid visiting websites that appear suspicious or untrustworthy. Look for signs like misspellings, unusual URLs, or requests for personal information that seem out of place.
- Use Strong Passwords: Create strong and unique passwords for each of your online accounts. A strong password includes a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. Avoid using easily guessable information like your name or birthdate.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: When available, enable two-factor authentication for your accounts. This adds an extra layer of security by requiring you to enter a unique code generated by your phone or a security key in addition to your password.
- Be Aware of Phishing Attempts: Phishing attacks attempt to trick you into revealing sensitive information like passwords or credit card details. Be cautious of emails or messages that seem too good to be true, or that ask for personal information that you wouldn’t normally provide.
User Experience and Frustration
Chrome freezes can significantly disrupt user experience and productivity. The sudden interruption of workflow, the inability to access information, and the frustration of waiting for the browser to respond can have a detrimental impact on user satisfaction.
Emotional Response of Users
Experiencing frequent browser freezes can evoke a range of negative emotions in users. The sudden interruption of work can lead to feelings of frustration, anger, and impatience. Users may feel a sense of helplessness as they struggle to regain control of their browser. In some cases, the repeated occurrence of freezes can lead to feelings of anxiety and even stress, especially if the user relies heavily on their browser for work or personal tasks.
Managing User Frustration
It is crucial to acknowledge and address user frustration when encountering technical issues. Here are some strategies to help manage user frustration:
- Provide Clear and Concise Information: Users appreciate being informed about the issue and the steps being taken to resolve it. Clear communication can help alleviate anxiety and build trust.
- Offer Practical Solutions: Instead of simply acknowledging the problem, offer users practical solutions they can implement to mitigate the issue. For example, suggest closing unnecessary tabs or restarting the browser.
- Emphasize User Empowerment: Give users control over the situation by providing them with options and choices. For example, allow them to choose between restarting the browser or waiting for a solution.
- Provide Support Channels: Ensure users have access to support channels, such as help articles, forums, or customer service, where they can seek assistance and share their experiences.
Future Trends and Browser Evolution
The landscape of web browsing is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changing user expectations. Understanding these trends is crucial for navigating the future of web browsing and the impact it will have on our digital experiences.
The Demise of Flash and its Impact on Web Browsing
The decline of Flash technology has significantly impacted web browsing, paving the way for a more streamlined and secure online experience. Flash, once ubiquitous for multimedia content and interactive applications, has faced criticism for its security vulnerabilities, performance issues, and lack of mobile compatibility.
- Increased Security and Stability: The removal of Flash has contributed to a more secure browsing environment by eliminating a major source of vulnerabilities. This has reduced the risk of malware infections and other security threats.
- Improved Performance: Flash was known for its resource-intensive nature, often leading to slow loading times and browser crashes. Its removal has resulted in faster and smoother web browsing experiences.
- Enhanced Mobile Compatibility: Flash was not designed for mobile devices, limiting its reach in the rapidly growing mobile internet market. The shift away from Flash has facilitated the development of mobile-friendly web content and applications.
Emerging Technologies and their Influence on Browser Performance
The rise of new technologies is shaping the future of browser performance, enabling faster loading times, richer user experiences, and enhanced security. These technologies are poised to revolutionize how we interact with the web.
- WebAssembly: This technology allows for the execution of code written in languages like C, C++, and Rust directly in the browser, offering significant performance improvements compared to JavaScript. It is particularly beneficial for computationally intensive applications and games.
- Service Workers: These JavaScript programs run in the background, enabling features like offline functionality, push notifications, and background synchronization. They enhance the user experience by providing faster and more responsive interactions, even in offline environments.
- WebXR: This technology allows for immersive experiences like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) directly in the browser. It opens up new possibilities for interactive content, gaming, and education.
Evolving Landscape of Web Development and its Implications for Browser Functionality
The web development landscape is constantly evolving, with new frameworks, libraries, and tools emerging to simplify development and enhance user experiences. These advancements have a direct impact on browser functionality, requiring browsers to adapt and support the latest web standards.
- Progressive Web Apps (PWAs): PWAs combine the best features of web applications and native mobile apps, offering a seamless user experience across multiple devices. Browsers are evolving to provide better support for PWAs, enabling developers to create more engaging and feature-rich applications.
- JavaScript Frameworks: Frameworks like React, Angular, and Vue.js have simplified front-end development, allowing developers to build complex web applications with ease. Browsers need to be optimized to handle the increased complexity and performance demands of these frameworks.
- Web Components: These reusable building blocks allow developers to create custom HTML elements, enhancing the flexibility and modularity of web development. Browsers are incorporating support for web components, enabling developers to build more efficient and interactive web applications.
Recommendations for Users
Experiencing Chrome freezes due to Flash files can be frustrating, but there are several proactive steps you can take to mitigate the issue and maintain a smooth browsing experience. By implementing these recommendations, you can minimize the impact of Flash on your browsing performance and ensure a more stable and efficient online experience.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
It’s essential to address potential issues proactively to prevent Chrome freezes caused by Flash files.
- Update Chrome Regularly: Keeping your Chrome browser up-to-date is crucial, as updates often include security patches and performance improvements that can address Flash-related issues.
- Disable Flash When Not Needed: Flash is known to be resource-intensive and can cause performance issues. If you don’t need Flash for a specific website, consider disabling it to conserve system resources.
- Clear Browser Cache and Data: A cluttered cache can contribute to performance problems. Regularly clearing your browsing data, including cache and cookies, can help optimize Chrome’s performance.
- Manage Extensions and Plugins: Some extensions or plugins can conflict with Flash or drain system resources. Disable unnecessary extensions and plugins to see if it improves performance.
- Check for Malware: Malware can affect your computer’s performance and potentially interfere with Flash. Run a full system scan with a reputable antivirus program to ensure your system is clean.
Alternative Solutions
If you encounter persistent issues with Flash, consider exploring alternative solutions that can enhance your browsing experience:
- Use a Different Browser: Some browsers, like Firefox, offer better Flash management and performance. Switching to a different browser might resolve your issues.
- Explore Flash Alternatives: Many websites are moving away from Flash and adopting HTML5, a more efficient and reliable technology. Look for websites that support HTML5 for a smoother experience.
- Contact Website Support: If you’re experiencing Flash-related issues on a specific website, contact their support team. They may have specific recommendations or solutions.
Additional Resources
For further information and support, consider these resources:
- Chrome Help Center: The Chrome Help Center offers comprehensive troubleshooting guides and answers to common questions. You can find information on Flash management, browser updates, and other performance-related issues.
- Adobe Flash Player Help: Adobe provides support and resources for Flash Player, including troubleshooting guides and FAQs.
- Online Forums and Communities: Online forums and communities dedicated to Chrome and Flash can be valuable resources for finding solutions and connecting with other users who have experienced similar issues.
Closing Summary
In a world where speed and efficiency are paramount, Chrome freezes can be a major inconvenience. While Flash files are a fading relic of the past, their presence can still disrupt your browsing experience. By understanding the potential issues they can cause, implementing troubleshooting techniques, and staying abreast of browser updates, you can minimize the chances of encountering these freezes. Remember, a smooth and responsive browsing experience is not just about technology; it’s about maximizing your productivity and enjoying the web without frustration.
Chrome freezing due to non-essential Flash files can be a frustrating experience, especially when you’re trying to get things done. This issue might be related to older hardware, like the processor found in the Samsung flip phone with the Snapdragon 808 , which may struggle to handle the demands of modern web pages.
If you’re experiencing Chrome freezing, consider updating your browser, disabling Flash, or even trying a different web browser altogether.
 Securesion Berita Informatif Terbaru
Securesion Berita Informatif Terbaru